One of the most common problems experienced by users of hosted email services is that they find they can only send email messages to their own domain.
For Example, if you have two hosted email addresses:
You find that you can successfully send an email message from one user to another, but when you try to send to any other domain:
You find that the email messages do not send.
Solution
You need to enable “Authentication” in your configured email account settings. There are many client email programs, probably the most common is Outlook.
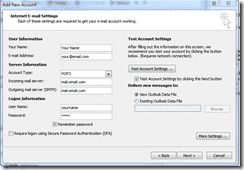
When you configure an new POP3 email account you normally end up with something that looks like this:
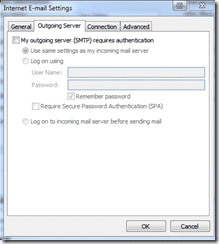
If you click on More Settings / Outgoing Server
and just tick the option to use the same settings as the incoming mail server.
This is all that is needed to enable outbound SMTP authentication.
Background
SMTP Servers (or email servers) are setup to need stop people using them for sending email messages. As strange as that sounds, if they were not setup this way, then anyone could SPAM the world using that email server.
To prevent users from abusing an Open Relay Mail Server, the administrators say that anyone wanting to send email messages from that server to any other server, will need a users name and pass. Almost always this is the same user and pass as the one needed to download your mail from that server.
This this need for user and pass is referred to as “Authentication” and is necessary on almost all servers, other than internet service providers who give you an internet connection. In that instance they authenticate you from your internet connection.
Why Can You Send to Your Own Domain?
Because Email Servers by nature will received email messages to addresses they host. This is part of the process necessary for email messages to be sent and received.